Pollutants in the environment and the workplace have a huge impact on our health and are key risk factors for cancer. Exposure to environmental pollutants such as particulate matter, occupational carcinogens, radon, and indoor air pollution, may be responsible for over one tenth of the total cancer burden in Europe.
However, exposure to environmental pollution varies widely across the EU and there are pronounced inequalities in the environmental impact on cancer burden.
The environmental module of the European Cancer Inequalities Registry supports the Zero Pollution Action Plan, particularly its flagship initiative focusing on "Reducing health inequalities through zero pollution". It aims to shed light on trends and disparities across the EU, to better inform and direct decision-making at EU, national, and local levels. The current indicator set integrates data on exposure to environmental pollutants and the related cancer burden.
Cancer deaths attributable to environmental factors
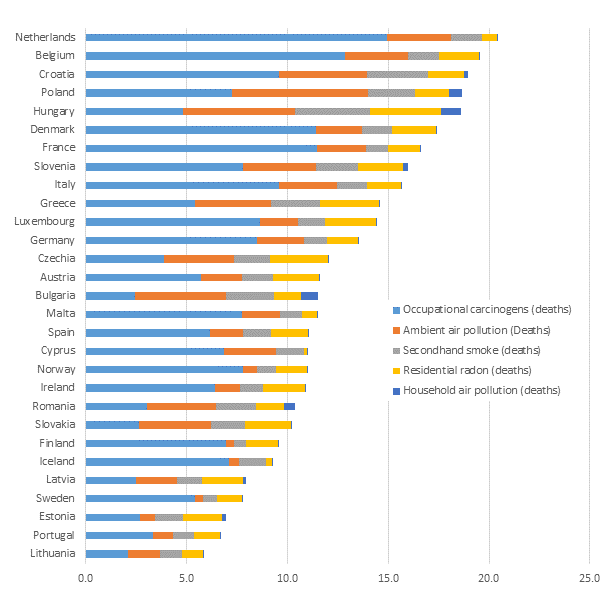
While some European countries are affected by a high level of environmental pollution overall, others face particular challenges in dedicated areas. For example, occupational carcinogens contribute to cancer deaths above the EU27 average in the Netherlands, Belgium, France, Denmark, Croatia and Italy. In contrast, radon represents a more significant burden of cancer deaths for Hungary, Czechia, Greece, Luxembourg, Austria and Slovenia, and the impact of second-hand smoke is more prevalent in the Eastern European region.
To learn more, check out the new Factsheet on the effect of environmental factors on cancer in Europe .
Explore the environmental indicators in the data tool
Cancer deaths from ambient air pollution
The indicator presents age-standardised death rate attributable to PM2.5
Cancer deaths from household air pollution
This indicator presents age-standardised death rate attributable to indoor air pollution from households
Cancer deaths from occupational carcinogens
This indicator presents age-standardised aggregated death rate attributable to occupational carcinogens
Cancer deaths from residential radon
The indicator presents age-standardised death rate attributable to exposure to radon
Daily exposure to tobacco smoke indoors
The indicator presents the proportion of people with a daily exposure to second hand smoke
Cancer deaths from passive smoking
The indicator presents age-standardised death rate attributable to second-hand smoke
Particulate matter 10
The indicator presents population-weighted annual mean concentration of particulate matter 10
Particulate matter 2.5
The indicator presents population-weighted annual mean concentration of particulate matter 2.5
Population weighted exposure to radon
The indicator presents the population-weighted average of radon concentration.
Deaths due to air pollution (time trend and estimation until 2050)
The indicator presents age-standardised death rate attributable to exposure to PM 2.5.
